| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |







scd23 SCD13 scd22 scd11
Infi
BDD electrode for waster water treatment and Water purifier production
BDD electrodes can effectively degrade various organic waste water, such as organic waste water in the fields of medicine /agrochemicals, petrochemicals, coking, smelting, printing and dyeing,
papermaking, tanning, explosives, wine making, landfill leachate, etc.
| No. | Product Name | Substrates | Specs | Unit |
| 1 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, single side coated | 5*5*0.55mm | Piece |
| 2 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, double side coated | 5*5*1.0mm 2 holes open | Piece |
| 3 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, double side coated | 5*5*1.0mm 4 holes open | Piece |
| 4 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, double side coated | 8*6*1 Slotting | Piece |
| 5 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, double side coated | 7*7*0.5mm | Piece |
| 6 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, single side coated | 10*10*0.625mm | Piece |
| 7 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, double side coated | 10*10*0.625mm | Piece |
| 8 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, double side coated | 10*10*0.5mm | Piece |
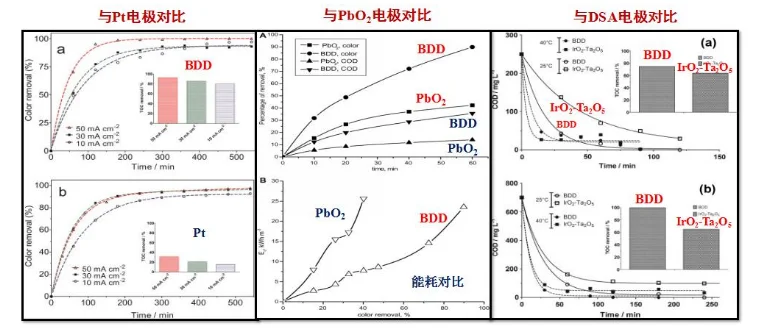
Under the same conditions, the efficiency and energy consumption of BDD electrodes in degrading organics are significantly better than other electrodes
Although using P b O 2 plates or P t nets as anodes can effectively generate ozone, they have disadvantages such as low durability, high price, and harmful effects to the environment. Boron-doped diamond (B D D) electrodes have also been reported to produce ozone without the use of any electrolyte. The applications of B D D in extreme electrochemistry, such as wastewater treatment and the synthesis of hydroxyl and methoxy groups, have been well documented. Due to its excellent chemical and physical stability, B D D is used in ozone-generated anode materials.
CVD diamond BDD Application:
Firstly, BDD has an extremely high bandgap (about 5.47 eV), much higher than silicon (1.1 eV), silicon carbide (4H SiC, 3.2 eV), and gallium nitride (GaN, 3.44 eV). This characteristic makes it an ideal material for manufacturing high-temperature and high-frequency electronic devices. Secondly, BDD has the highest thermal conductivity among all known materials, which not only increases the operating temperature range of the device, but also significantly reduces the size and weight of the device, which is beneficial for manufacturing high-performance amplifiers and lasers.
In addition, BDD has the highest electron saturation rate under high electric fields, and its hole mobility is also the highest among all wide bandgap semiconductor materials. These characteristics make BDD particularly suitable for millimeter wave amplifiers and high-speed integrated circuits. At the same time, BDD also has excellent electron emission capability and can achieve negative electron affinity after special treatment, making it an ideal choice for making cold cathodes.
Not only that, BDD also performs well in key semiconductor performance indicators such as Johnson index, Keyes index, and Baliga index. For example, its Johnson index is as high as 8200, far exceeding 4H SiC (410) and GaN (280). This means that BDD has unparalleled advantages in power amplifiers, integrated circuits, and switching devices.
BDD has a wide range of applications, covering flat displays, microelectronics MEMS/NEMS、 Strong electricity and electrochemistry, among other aspects. Especially in electrochemical sensors, BDD has become an ideal material for the new generation of high-performance electrochemical sensors due to its high conductivity, wide potential window, low background current value, and excellent anti pollution ability.
Polycrystalline CVD diamond
polycrystalline CVD (chemical vapour deposition) synthetic diamond products are manufactured by a chemical vapour deposition (CVD) process and are subject to tightly controlled growth conditions during manufacturing and equally stringent quality control procedures.
BDD electrode for waster water treatment and Water purifier production
BDD electrodes can effectively degrade various organic waste water, such as organic waste water in the fields of medicine /agrochemicals, petrochemicals, coking, smelting, printing and dyeing,
papermaking, tanning, explosives, wine making, landfill leachate, etc.
| No. | Product Name | Substrates | Specs | Unit |
| 1 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, single side coated | 5*5*0.55mm | Piece |
| 2 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, double side coated | 5*5*1.0mm 2 holes open | Piece |
| 3 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, double side coated | 5*5*1.0mm 4 holes open | Piece |
| 4 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, double side coated | 8*6*1 Slotting | Piece |
| 5 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, double side coated | 7*7*0.5mm | Piece |
| 6 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, single side coated | 10*10*0.625mm | Piece |
| 7 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, double side coated | 10*10*0.625mm | Piece |
| 8 | BDD Electrode | Silicon, double side coated | 10*10*0.5mm | Piece |
Under the same conditions, the efficiency and energy consumption of BDD electrodes in degrading organics are significantly better than other electrodes
Although using P b O 2 plates or P t nets as anodes can effectively generate ozone, they have disadvantages such as low durability, high price, and harmful effects to the environment. Boron-doped diamond (B D D) electrodes have also been reported to produce ozone without the use of any electrolyte. The applications of B D D in extreme electrochemistry, such as wastewater treatment and the synthesis of hydroxyl and methoxy groups, have been well documented. Due to its excellent chemical and physical stability, B D D is used in ozone-generated anode materials.

CVD diamond BDD Application:
Firstly, BDD has an extremely high bandgap (about 5.47 eV), much higher than silicon (1.1 eV), silicon carbide (4H SiC, 3.2 eV), and gallium nitride (GaN, 3.44 eV). This characteristic makes it an ideal material for manufacturing high-temperature and high-frequency electronic devices. Secondly, BDD has the highest thermal conductivity among all known materials, which not only increases the operating temperature range of the device, but also significantly reduces the size and weight of the device, which is beneficial for manufacturing high-performance amplifiers and lasers.
In addition, BDD has the highest electron saturation rate under high electric fields, and its hole mobility is also the highest among all wide bandgap semiconductor materials. These characteristics make BDD particularly suitable for millimeter wave amplifiers and high-speed integrated circuits. At the same time, BDD also has excellent electron emission capability and can achieve negative electron affinity after special treatment, making it an ideal choice for making cold cathodes.
Not only that, BDD also performs well in key semiconductor performance indicators such as Johnson index, Keyes index, and Baliga index. For example, its Johnson index is as high as 8200, far exceeding 4H SiC (410) and GaN (280). This means that BDD has unparalleled advantages in power amplifiers, integrated circuits, and switching devices.
BDD has a wide range of applications, covering flat displays, microelectronics MEMS/NEMS、 Strong electricity and electrochemistry, among other aspects. Especially in electrochemical sensors, BDD has become an ideal material for the new generation of high-performance electrochemical sensors due to its high conductivity, wide potential window, low background current value, and excellent anti pollution ability.
Polycrystalline CVD diamond
polycrystalline CVD (chemical vapour deposition) synthetic diamond products are manufactured by a chemical vapour deposition (CVD) process and are subject to tightly controlled growth conditions during manufacturing and equally stringent quality control procedures.